Undergraduate Psychology Program of UBAYA
The Undergraduate Psychology Program of UBAYA (UP-UBAYA) started to apply the higher education curriculum (Kurikulum Perguruan Tinggi – KPT), which in line with higher education (Program Studi – PS) undergraduate program curriculum act. By applying KPT, the establishment of learning outcomerefers to those stated in Indonesian National Qualification Framework (Kerangka Kualifikasi Nasional Indonesia – KKNI) level 6 based on President decree (Perpres) no 8 in 2012, higher education national standard as described in Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education regulation (Permenristek DIKTI) no. 4 in 2015, and the agreement of Indonesian Organizing Association of Higher Education in Psychology (Asosiasi Penyelenggara Pendidikan Tinggi Psikologi Indonesia – AP2TPI) in regard to qualification of Bachelor in Psychology as listed on SK 01/2015 AP2TPI.
Graduate profile of UP-UBAYA:
- Assistant manager
- Counselor
- Entrepreneur
- Trainer
- Community organizer
- Researcher
- Assessor
- Human resources
- Teacher (early childhood education, coaching, and consulting)
The learning outcome is determined by considering PS vision and mission, scientific vision, and tracer study in which all of them are stakeholders input (alumni and user of alumni, as well as student and lecturer feedback)
The Seven (7) Expected Learning Outcome (ELO) of Undergraduate Psychology Program of UBAYA (UP-UBAYA):
- Creating alternative problem-solving through analysis using basic concepts of psychological theory to describe and analyze issues and various non-clinical psychological phenomena in individuals, groups, organizations, and communities, especially urban communities.
- Applying basic psychological research, including research design, data analysis, and interpretation, and articulating conceptual thoughts and psychological research findings in the form of scientific writing in accordance with ethical norms and professionalism.
- Applying psychological assessments in analyzing psychological symptoms in individuals, groups, organizations, and communities, especially urban communities.
- Applying non-clinical interventions based on principles of behavior change in individuals, groups, organizations, and communities.
- Applying principles of data literacy, technology literacy, and community literacy.
- Creating, adapting, and developing psychological measurement and tests based on the principles of classical and modern test theories.
- Applying career and personal development plans, especially entrepreneurship.
The above UP-UBAYA’s ELOs are manifested into below curriculum structure:
CURRICULUM STRUCTURE OF UP UBAYA
The total credit a student should complete is 148 credits, accomplished in 8 semesters (4 years)
Semester I (Total 19 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
1500Z002 |
Pancasila and Civic Education |
3 |
|
1000C003 |
Religious Education |
3 |
|
14051104 |
Indroduction to Philosophy (Science and Logic) |
3 |
|
14051105 |
History and Schools of Psycology |
3 |
|
1500Z012 |
Human and Self Development |
3 |
|
1500Z013 |
Digital Literation |
2 |
|
1500Z014 |
Communicative English |
2 |
|
Total |
19 |
|
Semester II (Total 20 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14052106 |
Biopsychology |
3 |
|
14052107 |
Human and Moral Philosophy |
2 |
|
14052108 |
Psychology of Personality |
5 |
|
14052201 |
Child Development |
3 |
|
14052202 |
Introduction to Psychology |
3 |
|
14052401 |
Statistics |
4 |
|
Total |
20 |
|
Semester III (Total 19 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14053109 |
The Basics of Neuropsychology |
3 |
|
|
Adolescent and Adult Development |
3 |
|
14053205 |
Social Psychology |
3 |
|
14053301 |
Psychological Scale Development (4 |
4 |
|
14053501 |
Observation and Interview |
6 |
|
Total |
19 |
|
Semester IV (Total 18 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14054206 |
Organization Behaviour |
4 |
|
14054208 |
Group Dynamics |
3 |
|
14054302 |
Psychological Test Development |
4 |
|
14054402 |
Survey Research Methods |
3 |
|
14054502 |
Child and Adolescent Assessment |
4 |
|
Total |
18 |
|
Semester V (Total 21 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14053204 |
Educational Psychology |
3 |
|
14055503 |
Psychological Assessment of Adult |
4 |
|
14055211 |
Human Capital Management |
4 |
|
14055403 |
Qualitative Methods |
4 |
|
14055404 |
Experimental Methods |
3 |
|
|
General Elective Courses 1** |
3 |
|
Total |
21 |
|
Semester VI (Total 20 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14054207 |
Urban Psychology |
3 |
|
1301Z001 |
Entrepenenurship and Innovation |
3 |
|
14051103 |
Sociology and Anthropholgy of Industrial Society |
3 |
|
14056601 |
Learning and Develeopment in Organiations |
4 |
|
14056602 |
Coaching Mentoring, and Counseling |
4 |
|
14056603 |
Behaviour Modification |
3 |
|
Total |
20 |
|
Semester VII (Total 19 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14051101 |
Academic Indonesian |
3 |
|
14055210 |
Mental Health and Psychopathology |
4 |
|
14057505 |
Research Proposal |
3 |
|
|
General Elective Courses 2** |
3 |
|
|
General Elective Courses 3** |
3 |
|
|
Field Elective Courses 1*** |
3 |
|
Total |
19 |
|
Semester VIII (Total 12 Credits)
|
KODE |
MATA KULIAH |
Credits |
|
14054209 |
Exceptional Learners |
3 |
|
14057506 |
Undergraduate Thesis |
6 |
|
|
Field Elective Courses 2*** |
3 |
|
Total |
12 |
|
| General Elective Courses** | ||
| CODE | COURSES | Credits |
| 14058715 | Metode Penelitian Lanjut ** | 8 |
| 14058714 | Konflik Kerja Keluarga** | 3 |
| 14058713 | Kecerdasan dan Bakat Istimewa** | 3 |
| 14057712 | Keterikatan Kerja** | 3 |
| 14057711 | Manajemen Pengurangan Resiko Bencana** | 3 |
| 14057710 | Dukungan Awal Psikologi** | 2 |
| 14057709 | Psikometrika Terapan ** | 3 |
| 14057708 | Cyberpsychology** | 3 |
| 14056704 | Pendidikan alternatif ** | 3 |
| 14055707 | Psikologi Forensik** | 3 |
| 14055706 | Talent Management** | 3 |
| 14055705 | Intervensi bermain ekspresif ** | 3 |
| 14055703 | Psikologi Ekonomi ** | 3 |
| 14055702 | Psikogerontologi** | 3 |
| 14055701 | Psikologi Gender dan Feminis** | 3 |
| 1001C007 | Social Entrepreneurship and Innovation** | 6 |
| 1001C008 | Innovative Product Development** | 6 |
| 1001C003 | Community Leadership** | 6 |
| 1001C009 | Information Retrieval** | 3 |
| 1001C005 | Humanity Awareness Initiative** | 6 |
| 1001C004 | Disaster Resilience** | 6 |
| 1001C002 | Field Work Research** | 6 |
| 1000C011 | Start Up Busines Development** | 3 |
| Specific Elective Courses *** | ||
| CODE | COURSES | Credits |
| 14057604 | Penanganan Awal Perilaku Kecanduan*** | 3 |
| 14057605 | Terapan Psikologi Sekolah *** | 3 |
| 14057606 | Asesmen Individual dan Organisasional*** | 3 |
| 14057607 | Pemberdayaan Masyarakat Perkotaan*** | 3 |
| 14057608 | Dinamika Keluarga Urban*** | 3 |
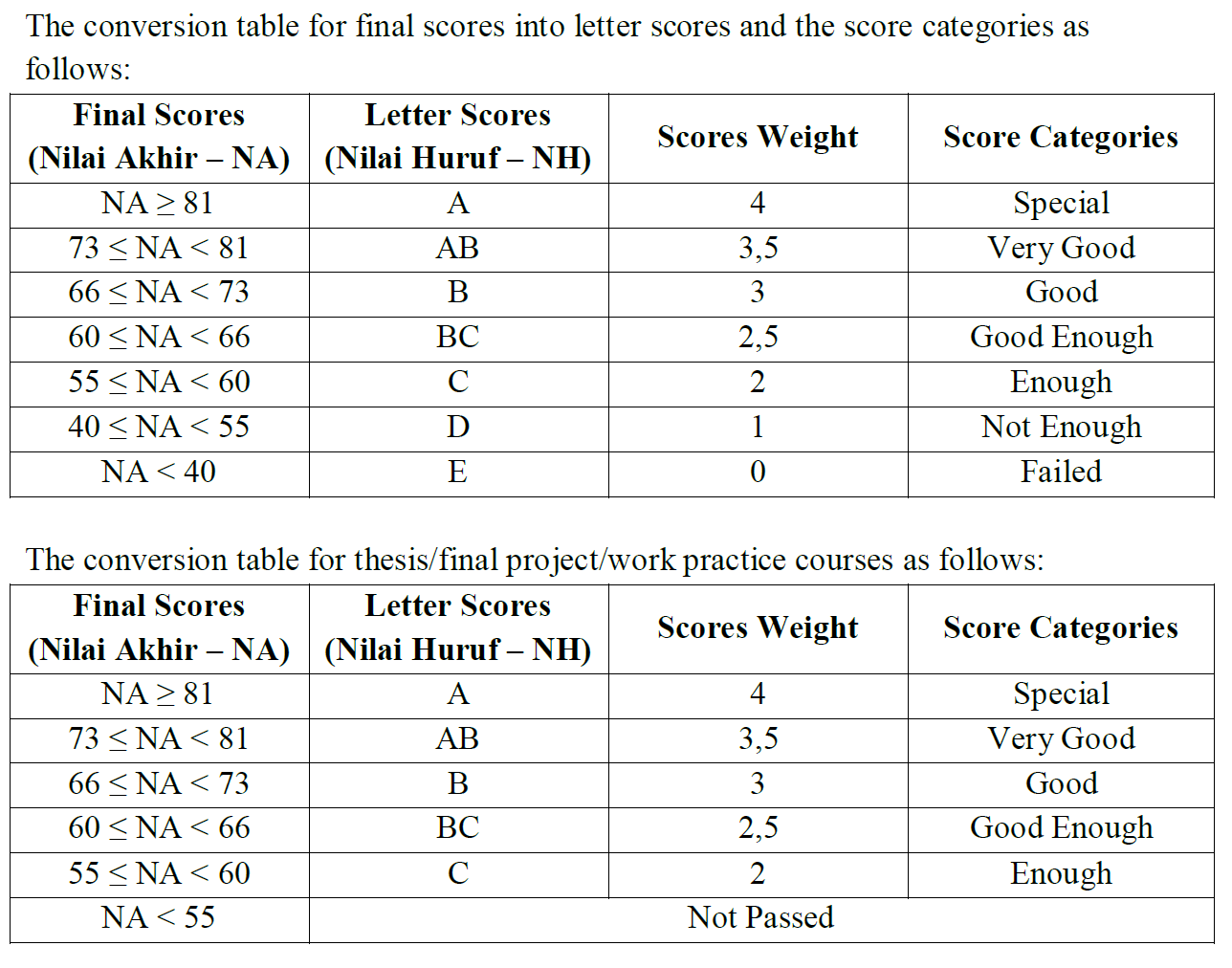
Grading System
The learning outcome will be measured through tracer study which invite the employer (user of the alumni) as the respondent. The survey measure PEO (Program Educational Objective) of the UP-UBAYA:
- Develop thinking skills, master the basic concepts of psychological theories, develop instruments of psychological assessment and research in psychology in order to describe and analyze various psychological problems in urban setting within the context of families, schools, industries, and communities based on the code of ethics for psychology in Indonesia.
- Conduct interviews, observation, and psychological assessments using the proper instruments as they are allowed and regulated by the principles and code of ethics of psychodiagnostics in Indonesia.
- Apply non-clinical psychological intervention methods aimed at changing the behaviors of individuals, organizations, and communities within the context of urban problems by employing counseling, psychoeducation, training, and other intervention techniques as they are allowed by the code of ethics of Psychology in Indonesia, inspired in practice by the spirit of continuous learning.
Referring to the Rector’s Regulation of University of Surabaya number 45 of 2013 on soft skill competencies, the alumni of UBAYA needs to master below soft skills:
- Self-management: the ability to control own’s behavior according to the personal goal and standard as well as the changing situation followed by the positive attitude in responding the situation so that he/she able to self-motivate and confidently keeps their goal on the track.
- Openness to diversity: the ability to respect and tolerate regardless ethnicity, religion, economic or social status, gender, etc.
- Communication: the ability to give and listen to opinion or idea systematically and logically based on context, both in verbal or written and whether between individuals or in public situation.
- Teamwork: the ability to cooperate with members coming from different characters and ability to identify the role of each members to accomplish mutual goal.
- Leadership: The ability to influence, help, and become role model in a positive way to accomplish mutual goal.
- Critical thinking: the skill which enable an individuals to utilize their knowledge and experience to identify and solve the problem in academic setting.
- Life-long learning: the ability to control own’s behavior according to the personal goal and standard as well as the changing situation followed by the positive attitude in responding the situation so that he/she able to self-motivate and confidently keeps their goal on the track. (penjelasan point 8 mirip dengan point 1, mohon dicek kembali file aslinya Bu)
- Integrity: ability to behave consistently based on organizational values and policies as well as academic ethics in any given situation. In other words, “do what is said”.
- Organizational skill (procedure): ability to learn and apply set of steps, policies or guidance needed to carry on typical task, responsibility or certain role.
Above soft skills are accomplished through:
- Curricular learning process
- Co-curricular activities (not listed in the curriculum but is a mandatory)
- Extracurricular activities (not listed in the curriculum and not mandatory)
Curricular activities are achieved through student center learning, in which it has less in-class lecture session and more working on assignment/project, role playing, and data collection. Using this method, students will develop and strengthen their soft skills.
Co-curricular learning starts when students: join in as a freshmen and involved in orientation period (Masa Orientasi Bersama – MOB) and GPB (Growing Personal Best) program held by the university, take part in EMSC (Exploring My Self Camp) in semester 2; participate in SHC (Self Help Camp) in semester IV; and participate in live in program during semester VI. Co-curricular which focus on sharpening student’s academic culture is achieved through students’ participation in student creativity program (Program Kreativitas Mahasiswa – PKM).
Extracurricular activities which are provided are sport (futsal, basket, volley, wushu), art (psychology of music, choir, dance, band), academic (pointer, student conference). Through participation in curricular, co-curricular and extracurricular will enable students to crystalize their knowledge, skill, and soft skill.